NR 511 Week 6 Quiz; Differential Diagnosis and Primary Care Practicum - 100% Correct
-
$20.00
| Institution | NR 511 Differential Diagnosis and Primary Care Practicum |
| Contributor | Alan Burton |
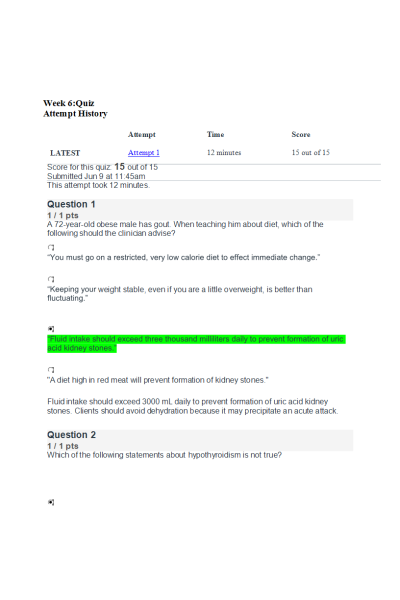
- Question: A 72-year-old obese male has gout. When teaching him about diet, which of the
following should the clinician advise?
- Question: Which of the following statements about hypothyroidism is not true?
- Question: Which of the following body mass index (BMI) values defines class 1 obesity?
- Question: The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is:
- Question: A low thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) can lead to:
- Question: A 24-year-old female is preparing for radioactive iodine therapy to treat Graves disease. Which test must she undergo first?
- Question: A client with hyperthyroidism presents with a complaint of a “gritty” feeling in her eyes. Over the past week, her visual acuity has diminished, and her ability to see colors has changed. She also has a feeling of pressure behind her eyes. The next step for the nurse practitioner is to:
- Question: A client presents with clinical manifestations of hyperthyroidism. The differential diagnosis includes Graves disease and subacute thyroiditis. Which of the following findings is consistent with subacute thyroiditis?
- Question: A 23-year-old female complains of palpitations that started a few weeks ago; they occur 2 to 4 times a day and last 5 to 10 minutes. She feels nervous and is having trouble sleeping. Her stools have been frequent (1-3 per day) and loose. She is taking levothyroxine 150 µg daily. Her labs indicate free thyroxine (FT4) 2.28 and thyroid- stimulating hormone (TSH) 0.022. She has a history of Graves disease and had radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment a few months ago. She has been on thyroid replacement for 2 months. Based on these findings, what should the clinician do next
- Question: A 46-year-old male presents with a tender, red and swollen knee. The clinician orders a complete blood count (CBC) with differential, uric acid level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Which of the following results would make the clinician suspect a septic joint rather than gout?
- Question: Alice, age 48, has a benign thyroid nodule. The most common treatment involves:
- Question: A 6-year-old girl was bitten by a friend’s dog. Her mother asks the clinician if the child needs anti-rabies treatment. Which of the following should the clinician advise?
- Question: Which of the following objective findings in a 49-year-old female is a sign of hyperthyroidism?
- Question: What is the medication of choice for an initial acute attack of gout?
- Question: An elderly client presents with atrial fibrillation. Which of the following lab tests is important in forming the diagnosis?
| Instituition / Term | |
| Term | Jul 2021 |
| Institution | NR 511 Differential Diagnosis and Primary Care Practicum |
| Contributor | Alan Burton |





-80x80.JPG)